PNS| HYDERABAD
Across the globe, Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are the most common bacterial infections affecting females. Due to lack of information, timely treatment is delayed and women undergo unnecessary suffering. More cases have been reported from the rural parts of India, where there is a lack of information, poor sanitary facilities, lack of hygiene, and inadequate healthcare access.
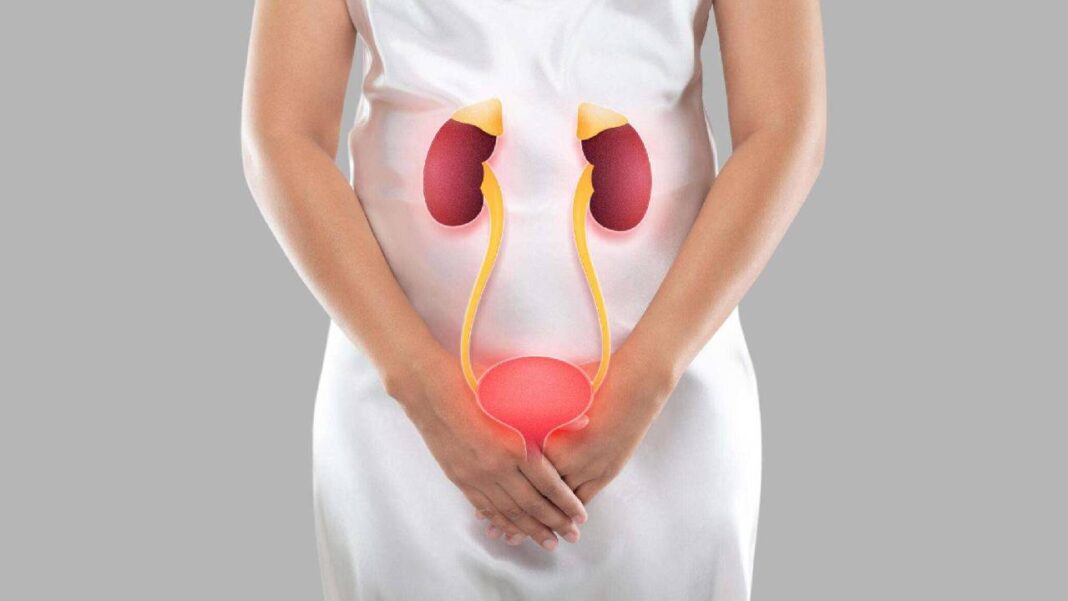
UTI is caused by a harmful bacteria called Escherichia coli. It enters the tract and multiplies. It affects the entire urinary tract which includes kidneys, ureters, bladders and urethra. Most common cases are recorded of bladder infections (cystitis) and urethral infections (urethritis).
Females are more vulnerable to UTIs than male population due to anatomical variation. The urethra in females is shorter, which provides an easy access for bacteria to enter the urinary tract. In addition to this, female hormones, sexual indulgence, pregnancy and other hygiene-based reasons increase the risk of UTIs.
Dr. Nivedita Jha, Consultant – Obstetrics and Gynaecologist, SPARSH Hospital for Women and Children, Infantry Road, Bangalore, shared primary symptoms of UTIs, which includes persistent urge to urinate, frequent but small amount, urination accompanied by burning sensation, strong odor, cloudy in colour, pain around the pelvic region, and sometimes accompanied by fever and chills.
Some of the popular common myths clouding the timely diagnosis of UTIs include, burning sensation during urination is caused due to intake of spicy food or body heat. There is no scientific evidence to prove the link between spicy food and UTI. In addition, it is also believed that such infections occur only to women who are sexually active, however it can affect women of all ages, ranging from young girls to elderly women. Improper sanitary hygiene, or even holding urine for too long can also cause infections. It is also believed that menstrual blood causes infections but it is partially true as using compromised sanitary products or infrequent change of pads during periods can elevate the risk of infection affecting the urinary tract.
Dr. Nikhat Siddiqui, Consultant Obstetrics and Gynecology, Apollo Spectra Hospital, Kanpur, warned that UTIs can turn serious and require immediate medical attention as untreated UTIs can lead to severe kidney infections, sepsis, and other long-term complications. Otherwise, oral medications like antibiotics can simply treat the issue. Untreated infections can pose higher risks during pregnancy, they can lead to premature labour, or even low birth weight in babies.
In India, there is a higher risk of UTIs due to lack of information and access to clean toilets. It is many-a-times associated with cultural taboos as seeking immediate help for symptoms related to urinary or reproductive organs seem inappropriate in traditional settings. Apart from this, rural or semi-urban regions lack clinics with female doctors due to which such issues are not diagnosed early. Due to which many women resort to self medication or even herbal remedies, which sometimes worsen the issue. It can also lead to recurrence of infection as proper treatment is not met.
UTIs have affected both rural and urban population, ranging from 3.14% to 19.87%. However, only around 40% of women in India reach out for medical help while experiencing symptoms related with reproductive tract infections, including infection of urinary tract.
It is important to remember that prevention is better than cure, and preventing UTIs is much easier than its treatment. Some of the practical solutions that must be adopted by women are maintaing proper hygeine of genital area, avoiding douching, frequent change of sanitary pads, staying hydrated to flush out the bacterial, do not hold urination for too long, and using comfortable cotton-based undergarments. Also, sexually active women must urinate shortly post intercourse, and clean the intimate area properly to avoid any infection.
It is necessary to avoid harsh products, specifically those scented or soaps in the genital areas. They tend to irritate and disturb the natural pH balance of the area. As per Dr. Poonam Agarwal, Principal Consultant, Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Sri Balaji Action Medical Institute, Delhi, it is advised to intake a balanced diet which is rich in Vitamin C, with probiotics like curd, and fiber rich food to boost a healthy immune system.
Other conditions like kidney stones or diabetes can increase the risk of UTIs. It is necessary to come in contact with a medical expert, gynecologist or urologist to get immediate medical care and prompt treatment. A simple urine test (urine culture) can conclude the presence of bacteria causing infection. Generally, antibiotics are prescribed to get rid of such bacterial infections. However, recurring urinary tract infections require intensive investigation through radiology-based equipment, like ultrasound or cystoscopy.
It is important to understand that UTIs are easily preventable and common across the globe. Following simple hygiene practices, adopting clean eating habits, bursting myths associated with genital health, and enhancing access to healthcare can result in a decrease in the number of reported severe cases of UTIs and other concerns related with urinary tract health.